It wasn't just President Barack Obama who won Tuesday. His signature health care plan did as well. Photo by Courtesy Pete Souza
It wasn't just President Barack Obama who won Tuesday. His signature health care plan did as well. But while the Affordable Care Act remains alive, less clear is how its various mandates will proceed and who will participate.
To a large extent, the success of the health overhaul lies in how many of the nation's uninsured get coverage. And that is largely in the hands of the states, which have been all over the map in their willingness to cooperate.
We mean that literally. The maps here show the lack of consensus on two key parts of the act: Creating insurance exchanges and expanding Medicaid.
Here's why each map matters.
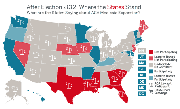
Map 1: Where Will We Buy Insurance?
Source: Kaiser Family Foundation
The health care act requires all Americans who aren't already insured to buy coverage. But where? That's where insurance exchanges come in.
States have to decide whether to set up these online marketplaces, where individuals can choose among different insurance plans. Setting up an exchange allows states to customize the offerings to the needs of their residents.
States can also partner with the federal government on exchanges. But if they elect not to, the federal government will take over with its one-size-fits all exchange. States are supposed to decide which course to take by Nov. 16.
Along the West coast, legislatures have already voted to set up exchanges. Other states, including Texas, Maine and Alaska, have decided to punt.
But many states in the Midwest and South haven't committed either way. Some governors, such as New Jersey's Gov. Chris Christie, have held off setting up a state insurance exchange until after the election.
A health care consultant group predicted yesterday that 20 states will elect to operate exchanges.
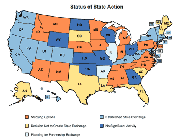
Map 2: Will States Cover More Poor People?
Source: The Advisory Board Company
Obamacare hopes to expand coverage to 30 million of the country's 48 million uninsured residents. A big part of that would come though Medicaid.
States must also decide whether to expand Medicaid to all residents under 133 percent of the federal poverty line (about $14,893 for an individual and $30,657 for a family of four). Medicaid currently covers poor children, pregnant women, seniors and some disabled adults. The federal government will pay the full cost for the expanded coverage for three years, and then gradually reduce its contribution to 90 percent over the next three years.
As passed in 2010, the Affordable Care Act required states to expand Medicaid or risk losing all federal matching funds for the program. But the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in June that it was coercive to force states to expand their program just to keep money they were already getting.
Now, states that don't opt in will keep their current funding, but residents who might have qualified under an expansion will likely remain uninsured. There isn't a deadline for the expansion, but the federal government says states will receive less federal help if they decide to expand later, according to The New York Times.
As with exchanges, the states are divided.
So far, a handful 2013 including California, Washington and Illinois 2013 have already embraced the expansion. Florida, South Carolina, Mississippi and Louisiana and Wisconsin have opted out.
Too Murky to Map
Not everything is left to states. Other issues remain murky about the law, perhaps because the deadlines are further in the future.
The requirement for individuals to either buy insurance or pay a fee to the IRS begins Jan. 14, 2014. But the federal government has not made clear how vigorously it plans to pursue those who don't comply.
Here's a flow chart showing who has to pay and who doesn't.
Also unclear is the impact on employers, who will be required to provide health insurance to full-time workers beginning in 2014. Some, according to The Wall Street Journal, are responding by moving employees to part-time positions.
- Have you or a loved one been harmed in a medical facility? Share your story with us.
- Are you a medical provider? Tell us what you've observed about patient safety.



Comments
Use the comment form below to begin a discussion about this content.